Part:BBa_K3182107
Contents
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 653
Illegal BamHI site found at 580 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Introduction
pT7-CBDcipA-Pln1

This part consists of a carbohydrate binding domain (CBD) from Clostridium thermocellum (C. thermocellum) cellulose scaffolding protein (CipA). This binding domain is a central part of Clostridium thermocellum's cellusome and has a strong affinity for cellulose. The CBD was fused to another protein using a flexible GS-linker (-GGGGSGGGGS-) in order to attach this complex to a polysaccaride material. A thrombin cleavage site (-LVPRGS-) was added to the end of the linker and its breakage will leave a glycine and serine attached to the N-terminal of the fusion protein. The main mechanism of iGEM19 Linköping's project can be seen in Figure 1.
Protease site and use
The thrombin site was added to enable the ability to release the fusion protein down into skin wounds. Thanks to our integrated human practice we learned that infections span much deeper into wounds that we thought. Simply attaching the CBD-fusion protein to a carbohydrate material would not enable the fusion protein to reach far into the wound. The thrombin site was also chosen because of thrombin's endogenous existence in humans.
Assembly compabilities
An internal BamHI recognition sequence (RS) has been added to enable interchangeable fusion proteins to the CBD. BamHI was chosen because its RS codes for glycine and serine, fitting it to the end of the thrombin site. It is also a cost-effective enzyme and is unaffected by methylated DNA. BamHI is a part of the RFC21 standard.
CBDcipA crystal structure
Important molecular faces
CBDcipA is composed of a nine-stranded beta sandwich with a jelly roll topology and binds a calcium ion, which can be seen in Figure 2. It further contains conserved residues exposed on the surface which map into two clear surfaces on each side of the molecule. One of the faces mainly contains planar strips of aromatic and polar residues which may be the carbohydrate binding part. Further aspects are unknown and unique to this CBD such as the other conserved residues which are contained in a groove.
Carbohydrate binding domain specificity
Since the CBD is from the cellusome of C. thermocellum some research labeled it a cellulose binding domain. However, iGEM19 Linköping noticed that this domain could also bind to different sources of polysaccaride materials. This serves as a domain for iGEM19 Linköpings modular bandage, where the polysaccaride material can be exchanged for other/similar materials and not exclusively cellulose.
The choice of carbohydrate binding domain
iGEM Linköping 2019 chose CBDcipA due to the fact that many other iGEM teams had explored the possibilities of this domain. Our basic design was influenced by [http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial iGEM14 Imperial], [http://2015.igem.org/Team:edinburgh iGEM15 Edinburgh] and [http://2018.igem.org/Team:ecuador iGEM18 Ecuador]. Purification and where to place the fusion protein (N- or C-terminal) was determined by studying the former projects. CBDcipA also originates from a thermophilic bacteria which further increases the domain's applications.
Expression system
The part has a strong expression with a T7-RNA-polymerase promotor (BBa_I719005), seen in Figure 3, as well as a 5'-UTR (BBa_K1758100) region which has been shown to further increase expression in Escherichia coli (E. coli) (BBa_K1758106), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2676996 Olins et al. 1989]), ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23927491 Takahashi et al. 2013]).

Antimicrobial Agent - Pln1
Fused to the CBD is a Lactobacillus plantarum antibacterial peptide 1. The peptide is 38 amino acids long and has a secondary structure closely resembling membrane proteins. The function of Pln1 is to inhibit competing bacteria. The antimicrobial peptide has not been studied extensively but is thought to have an α-helical C-terminal and amphiphilic characteristics. The N-terminus consists probably of a random coil (therefore no stable structure outside the cell membrane) and and has a more hydrophilic nature. With this overlay of Pln1 is has a capability to disrupt membrane bilayers and associate themselves in pore formation inside it and therefore permeabilisation of the membrane leading to lysation of the bacteria. Pln1 has been reported to have better activity to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE), Micrococcus luteus and same activity to Staphylococcus aureus compared to nisin. Therefore, Pln1 in combination with nisin or by replacing it could be a lucrative candidate.
The peptide is designed to battle the Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp. family of pathogens (ESKAPE). ESKAPE is a family(s) of bacteria which has multiple substrains that has evolved resistance to the most commonly used antibiotics.
Usage and Biology
The desired function of this construct is that the CBD will allow a more efficient expression of antimicrobial peptides by being a hydrophilic anchor to the bactericidal peptide or enzyme. The CBD can be used for easy purification of the fusion protein and via thrombin cleavage of the linker, yield the peptide or enzyme only. In iGEM19 Linköping's project the thought was to create an antimicrobial bandage by having a polysaccharide based bandage with CBD-antimicrobial agents bound to it. When applying the bandage to a patient, the patient's blood (containing thrombin) will release the peptides or enzymes into the wound (thrombin sprays used in hospitals can be used as well) leading to the activation of the peptide/enzyme and enabling them to reach the bacteria, thus eliminating the infecting pathogens.
Expression, purification and protease treatment
The antimicrobial agents which iGEM19 Linköping used were all expressed the same way. Early expression experiments showed great promise but with low yields. The early experiments were done with standard E. coli BL21 (DE3) expression, cultures were grown to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.4-1.0 in varying volumes and induced with 0.5 mM IPTG. Induced cultures were left to express the agents for 16 hours in 18 °C. Harvest of the cells was done at 3500 rpm for 30 minutes.
Solubization and purification
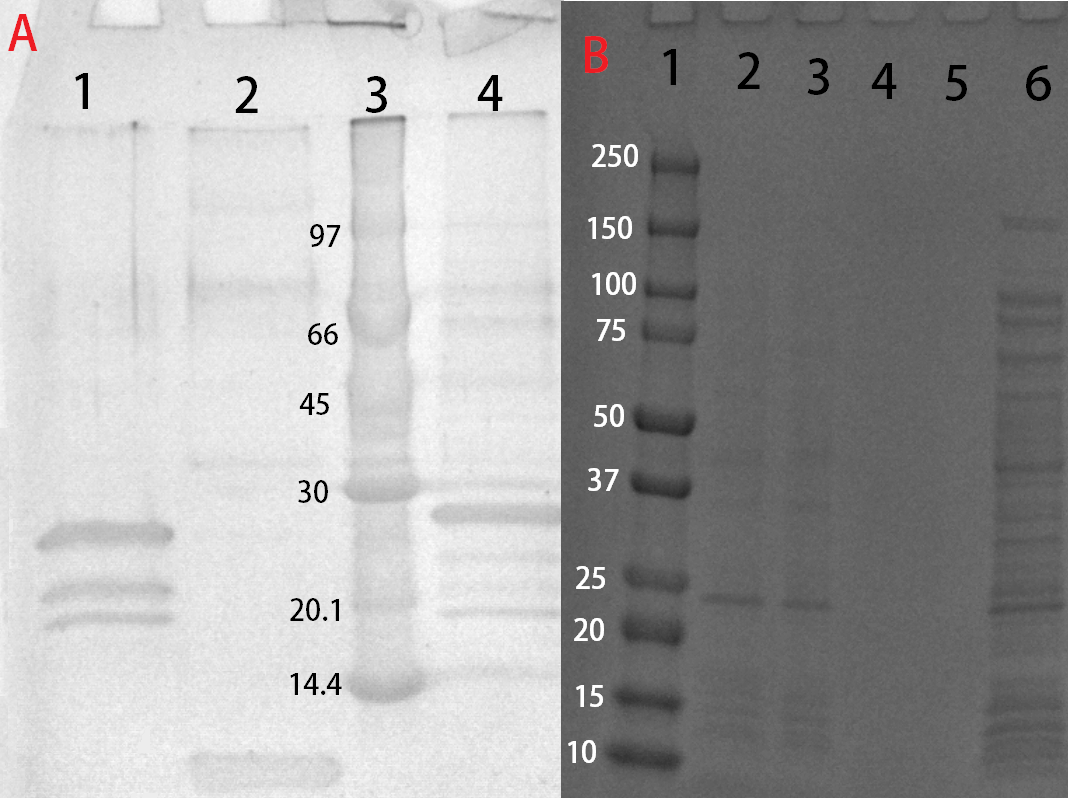
After harvest the cells were re-suspended in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, NaCl 137 mM, KCl 2.7 mM, Na2HPO4 10 mM, KH2PO4 mM) buffer or carbohydrate binding module buffer (CBM-buffer, Tris–HCl pH 7.0, 20 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2) and sonicated for 6 minutes, 30 % amplitude and 30 seconds on, 30 seconds off. The sonicated bacteria were then centrifuged at 12000 g for 15 minutes. The soluble fraction was then purified by attaching the CBD-fusion to cellulose. This showed very faint bands on SDS-PAGE analysis. Because of the low yield from the soluble fraction, a detergent (Triton X100, 1 %) was used to re-suspend the lipid-soluble proteins (insoluble fraction).
The Triton-X100 1 % fraction was later bound to microcristallin cellulose by Sigma Aldrich. A culture of 1 L E. coli BL21 (DE3) treated as above and lysed in 60 mL CBM-buffer. Half of that amount was then incubated with 5 g of microcristallin cellulose for 2 hours in 4 °C. After binding the CBD-fusion protein to the cellulose, washing was done with either 70 % ethanol, PBS- or CBM-buffer. Where 10 mL of each solution was added and incubated with the cellulose for 30 minutes. This step was repeated three times to remove unbound proteins and any residual Triton X100. After washing, elution was done with deionized water. A volume of 10 mL was sufficient to elute some CBD-fusion proteins (room temperature), while others needed higher temperatures (37 °C). This was done in 50 mL tubes under shaking. In hindsight, a column should be used to better track the elution.
Thrombin treatment
These bound fractions could also be cleaved with thrombin, where 25 units Bovine Thrombin (100 µL) by Sigma Aldrich was added. To this thrombin cleavage buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl and 2.5 mM CaCl2) was also added (500 µL) along with deionized water (4.4 mL). The cellulose bound fraction was discarded and the supernatant, with thrombin and the now unbound antimicrobial agent, was saved for later use. The results from this can be seen in Figure 4.
Antimicrobial activity agents in different states
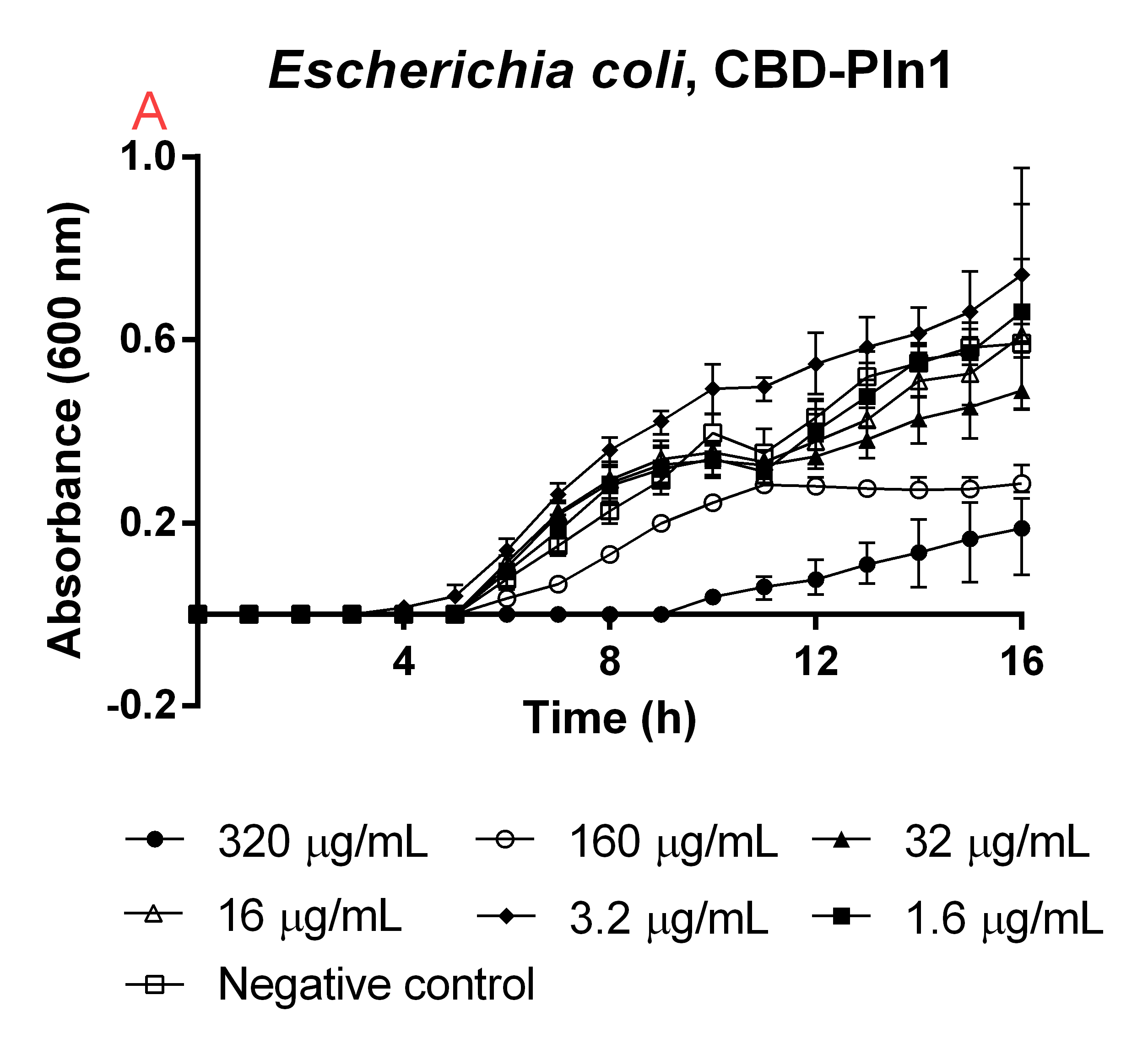
All experiments below used E. coli BL21 (DE3) or Bacillus Subtilis in concentrations of 10000 CFU/mL. This was done in order to get starting cultures of 0 OD600. Using spectrometry to measure the time until the bacteria started growing, instead of showing the killing capability on high optical density cultures, mimicked early stage wounds. This also showed many other interesting things, which can be seen in the results below. One being that an equilibrium settled in lower than for the negative control, meaning that even though the antimicrobial agents could not inhibit the growth fully, it was slowed and the stationary phase was reached earlier (Figure 5, 6B).
CBD bound agents
An experiment to test the antimicrobial activity of our agents still bound to the CBD was conducted, which can be seen in Figure 5. This was done in order to see if the absence of thrombin cleavage would yield inactive agents. The CBD-bound agents were purified like the method above mentions. Six technical replicates of E. coli BL21 (DE3)(160 µL in low salt LB-media, 0.4 g/L NaCl) were added to a 96-well plate by Eppendorf. To this 40 µL water was added to function as a negative control (called negative control in Figure 5). To 6x6 wells a concentration gradient was added in the same way, always adding 160 µL (in low salt LB-media) E. coli BL21 (DE3) and 40 µL of the unbound agents in water, diluted to the concentrations in Figure 5. The experiment was run for 16 hours in 37 °C and before each measurement a quick shake (200 rpm, 10 seconds) was done. The absorbance at 600 nm was measured every hour.
Importance of testing the CBD-bound agents
High amounts of the CBD-bound agent could still inhibit growth of E. coli BL21 (DE3), meaning if thrombin is not present in the wound the bandage would still yield a antimicrobial effect, this can further be seen in Figure 5. This also explains the trouble when expressing the CBD-agents and why they can be found in the insoluble fraction.
Antimicrobial activity of unbound agents
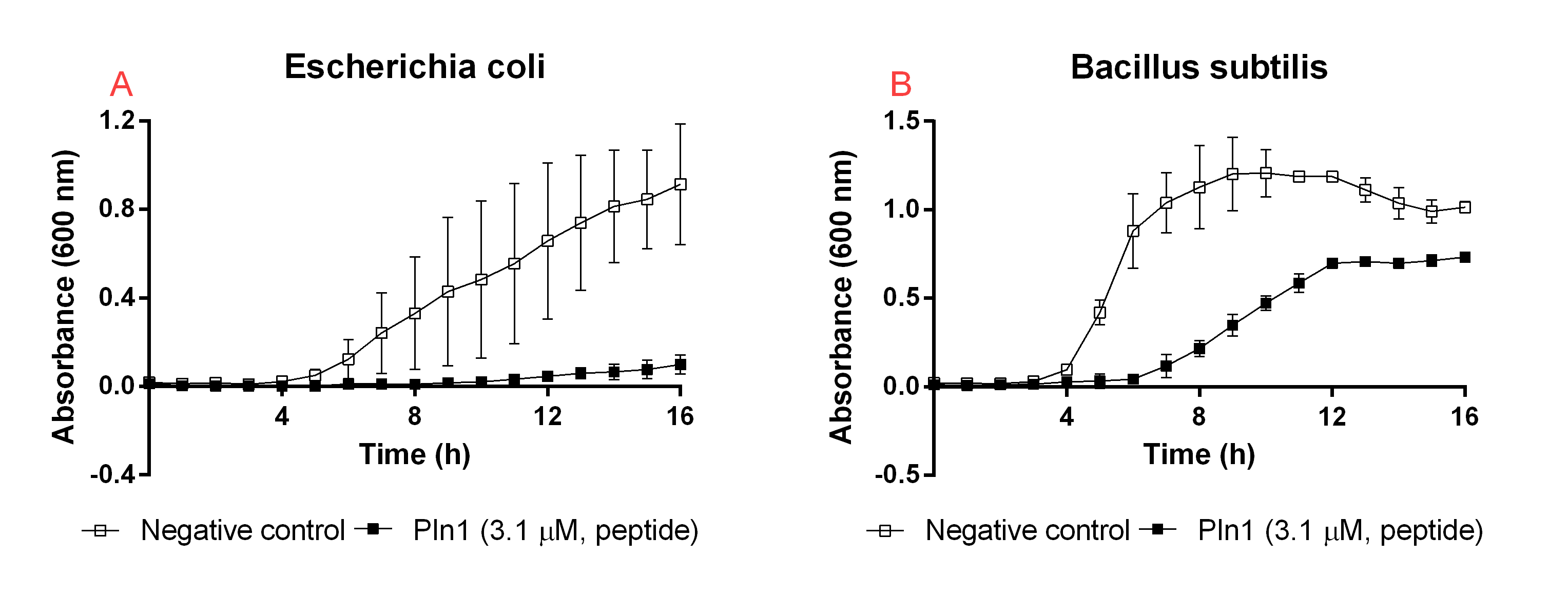
Unbound agents
As a positive control before starting our experiments with the CBD-agent-bandage, the unbound agents were tested for antimicrobial activity when they were not bound to the CBD. The results from this experiment can be seen in Figure 6. The agents were purified and treated with thrombin as stated before. The experimental setup was the same as the earlier experiment but instead of adding water to the negative control, thrombin (0.5 U, final concentration 0.6 µM) and thrombin cleavage buffer (40 µL, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl and 2.5 mM CaCl2) was added. This was because the agents had thrombin and cleavage buffer with them. This showed to not affect the bacterial growth, but rather increase it due to the added salt due to the cleavage buffer.
Antimicrobial activity immobilized and released

Immobilization and release on a cellulose bandage
To show the proof of concept for iGEM19 Linköping's project, the antimicrobial agents were fused to a cellulose bandage (Epiprotect by S2Medical). The cellulose was first incubated with E. coli BL21 (DE3) lysate (20 mL) containing CBD-Pln1 or CBD-PlyF307 for two hours in 4 °C. After immobilization of the agent to cellulose, the cellulose was washed three times with carbohydrate binding module buffer (CBM-buffer, 10 mL, Tris–HCl pH 7.0, 20 mM NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2). After washing, small pieces of bandage were cut out to fit into wells in a 96-well plate. Added to this well was also low salt LB-media (160 µL, 0.4 g/L NaCl) containing E. coli BL21 (DE3) at 0 OD600. Thrombin cleavage buffer (40 µL, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl and 2.5 mM CaCl2) without thrombin was added to all wells, keeping the CBD-agent immobilized on the cellulose. To wells where the agent would be released into solution, thrombin cleavage solution (40 µL, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2 and 0.5 U thrombin, final concentration in well 0.6 µM) was added. The negative control included thrombin cleavage solution (40 µL). In Figure 7, the results from this experiment can be seen. Noticeably, the thrombin released agent inhibited the E. coli growth the most of the combinations tested. This shows that the proof of concept of iGEM19 Linköping's main mechanism is working.
Thrombin accessibility in wounds
The thrombin used for releasing the agents into the solution had a concentration of 0.6 µM, this was to mimic the concentration found in blood from wounds. According to ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12871286 K.G Mann et al. 2003]) the concentration of active thrombin during clotting is several hundred nanomolar, depending on the age of the wound. In the experiment above, thrombin concentrations used was 600 nM. This hopefully mimics a real wound as closely as possible, while working in vitro.
| None |

